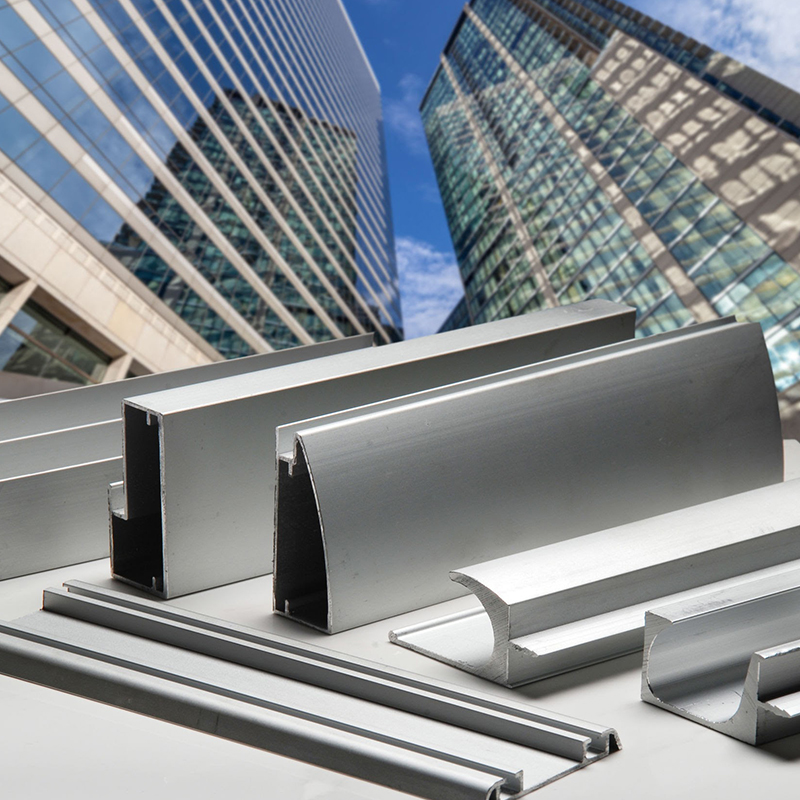
Aluminum profiles are foundational elements in modern architecture, engineering, and product manufacturing. Their unique combination of lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and adaptability makes them ideal for a wide array of applications, ranging from structural frameworks to intricate electronic housings. As industries push for more efficient, durable, and cost-effective materials, aluminum profiles—especially precision-formed shapes like aluminum Z profiles, U-shaped aluminum profiles, and aluminum T profiles—are rapidly becoming the go-to solution. This article delves into the core aspects of aluminum profiles, including how they’re made, their properties, specifications, and key industrial uses.
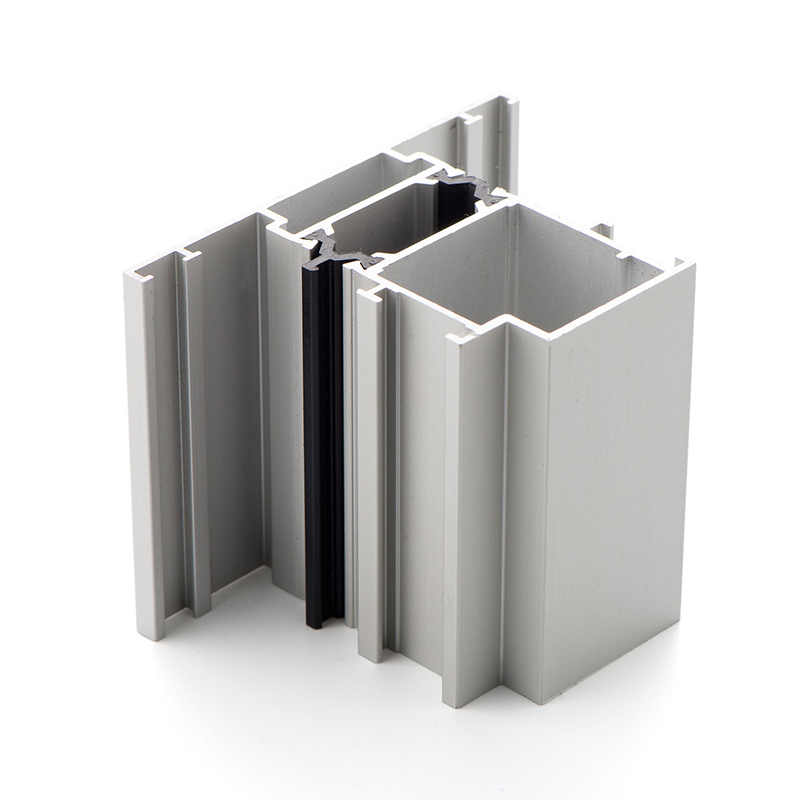

What Is an Aluminum Profile?
An aluminum profile refers to a precisely shaped piece of aluminum produced through a process called extrusion. These profiles are manufactured to have specific cross-sectional designs, enabling them to perform structural or functional roles in machinery, construction, electronics, or consumer products. Common variations include aluminum H profiles for framing, U channel aluminum profiles for enclosures, and aluminum Z profiles used in cladding or mechanical support systems.
Aluminum profiles are widely favored because of their geometric consistency and the ability to be engineered to exact specifications. Whether a customer needs lightweight, corrosion-resistant framing for a solar panel mount or a precision-machined enclosure for electronic components, aluminum extrusion profiles provide the flexibility to meet such demands with remarkable efficiency. Each profile is designed not just for function, but also for compatibility with other components in a modular or integrated system.
How Are Aluminum Profiles Made?
The primary process used to manufacture aluminum profiles is extrusion. In this process, a solid aluminum billet is heated until it becomes malleable but not molten—typically around 400°C to 500°C. The billet is then pushed through a hardened steel die using a hydraulic press. The shape of the die determines the cross-section of the resulting profile.
As the material emerges from the die, it takes on its final shape and is rapidly cooled using fans or water spray to solidify the profile quickly and maintain dimensional accuracy. Once cooled, the long aluminum profile is stretched to straighten it and then cut to standard or custom lengths. After cutting, the profiles often undergo additional treatments such as anodizing, powder coating, or mechanical polishing, enhancing both appearance and resistance to environmental factors.
This manufacturing method allows for the creation of complex and high-performance products like aluminum T profiles, U-shaped aluminum profiles, and specialized aluminum Z profiles with high precision and low material waste. The flexibility of aluminum extrusion makes it possible to produce large volumes efficiently while also enabling highly customized solutions tailored to specific industrial needs.
What Are the Basic Characteristics of Aluminum Profiles?
Aluminum profiles possess a unique set of physical and mechanical properties that make them superior to many alternative materials. First and foremost, aluminum is extremely lightweight, weighing approximately one-third as much as steel, making it ideal for applications where reducing weight is critical—such as in transportation or aerospace.
In addition to its low weight, aluminum exhibits excellent corrosion resistance. When exposed to air, it naturally forms a thin oxide layer that protects the metal beneath from further degradation. This characteristic makes u channel aluminum profiles and other shapes suitable for outdoor use, even in marine or humid environments.
Another key attribute is high strength-to-weight ratio, which allows aluminum profiles to support significant loads while remaining light and manageable. Aluminum is also a good conductor of electricity and heat, which is especially valuable in the production of heat sinks or electronic casings using aluminum extrusion profiles.
Moreover, aluminum is incredibly malleable, allowing manufacturers to create intricate profile designs without compromising structural integrity. It can be easily cut, machined, drilled, or welded, which simplifies assembly in the field or on the production line. Additionally, aluminum is 100% recyclable, making it an eco-friendly option for industries focused on sustainability.
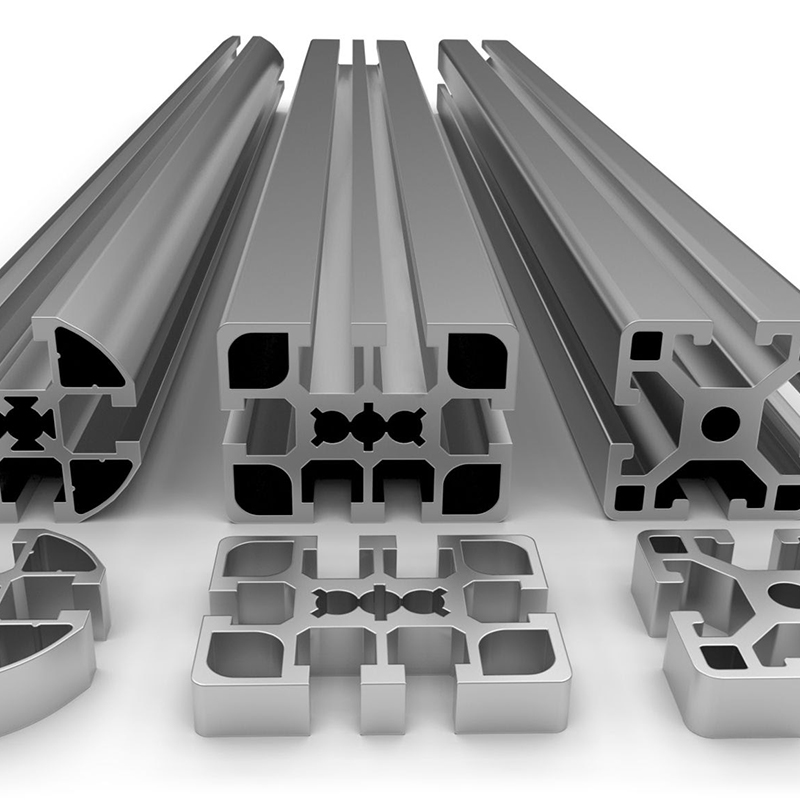
How Do Aluminum Z Profiles Differ from Aluminum Profiles Made of Other Metals?
When comparing aluminum Z profiles to similar profiles made of materials like steel, copper, or brass, several distinct advantages become apparent. The first is weight: aluminum is significantly lighter than most metals, which makes transportation, installation, and structural design more efficient and less costly. For instance, in curtain wall systems or roofing structures, using Z profile aluminum reduces the overall load on the framework, improving longevity and safety.
Unlike steel, aluminum does not rust. Its natural oxide layer resists corrosion without the need for extensive protective coatings. This gives aluminum profiles a longer service life with minimal maintenance, particularly in outdoor or coastal applications.
Aluminum also offers better fabrication ease. It can be extruded into complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to produce in harder metals. This makes it ideal for custom Z profiles, U-shaped channels, or T-profile systems where precision and form complexity are essential.
While copper and brass have excellent conductivity, they are considerably more expensive and prone to oxidation. Aluminum offers a cost-effective balance of conductivity, mechanical performance, and durability—making it a preferred material in electrical and mechanical applications alike.
What Are the Common Uses of Aluminum Profiles?
Due to their versatility and adaptability, aluminum profiles are used across a wide range of industries. In the construction sector, they’re commonly found in doors, windows, curtain walls, and facade systems. For example, aluminum H profiles are often used as structural joiners, while U channel aluminum profiles are utilized for framing glass panels or partitions.
In transportation, aluminum profiles are used to build lightweight structural elements in vehicles, ships, and airplanes. The reduced weight improves fuel efficiency without sacrificing strength. In furniture manufacturing, designers often prefer aluminum U profiles for modular shelving, support beams, and stylish trim pieces thanks to their clean lines and modern appearance.
In the electronics industry, aluminum’s thermal conductivity makes it ideal for use in heat sinks and enclosures that protect sensitive components. Custom aluminum extrusion profiles allow manufacturers to create compact and efficient cooling systems.
In renewable energy, U-shaped aluminum profiles are essential in mounting systems for solar panels, where they provide strong, corrosion-resistant support that can withstand harsh outdoor conditions. Other niche uses include z profile aluminum for mechanical linkages and T profiles in sliding systems and assembly lines.
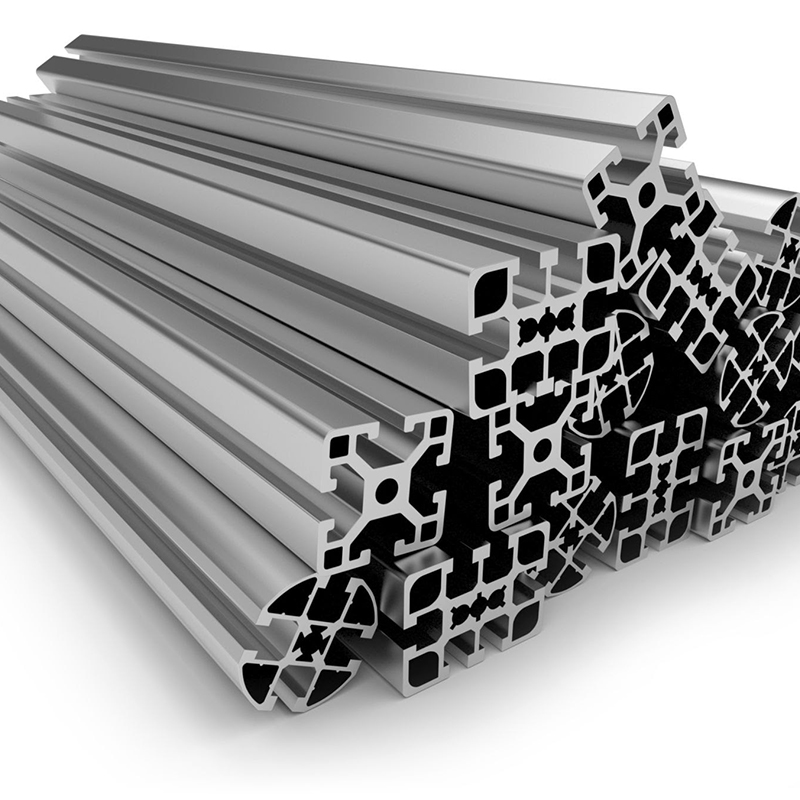

What Are the Main Specifications of Aluminum Profiles?
Aluminum profiles can be customized in nearly every aspect to meet specific project needs. The shape of the profile is one of the first variables, with standard types including Z, U, T, H, L, and a wide array of complex custom geometries. Each is selected based on the structural or functional requirements of the application.
The alloy type is another important factor. Common aluminum alloys used in profiles include 6061 and 6063, both of which provide a good balance of strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance. For applications demanding higher strength, 7075 alloy may be used.
Surface treatment options are also varied. Many profiles undergo anodizing for enhanced corrosion resistance and appearance. Others are powder-coated to achieve a specific color or texture. Some applications require mill finish profiles where raw aluminum is suitable, or brushed finishes for decorative purposes.
In terms of dimensions, aluminum profiles can be produced with wall thicknesses ranging from 0.8 mm to more than 5 mm, depending on the load requirements. Lengths are usually available in 3–6 meter sections but can be cut or fabricated to custom lengths. Tolerances on critical dimensions are typically tight, especially for industrial or precision applications involving interlocking profiles or moving parts.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum Profiles?
There are numerous advantages to using aluminum profiles, especially when compared to other building and structural materials. First is the ability to create complex cross-sectional shapes through extrusion, enabling engineers and architects to design solutions that combine form and function without compromise.
Durability is another key benefit. Aluminum’s corrosion resistance and structural integrity mean that it can withstand harsh environmental conditions without degradation over time. This makes it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications, including aluminum H profiles in industrial framing systems and U shaped aluminum profiles in architectural installations.
Ease of assembly is also a strong selling point. Many aluminum profiles are designed with modularity in mind, allowing for quick installation with minimal tools or fasteners. This reduces labor costs and shortens project timelines.
From an environmental perspective, aluminum is highly sustainable. It is 100% recyclable and retains its properties through multiple reuse cycles, making it an environmentally responsible choice for eco-conscious projects.
Finally, aluminum profiles offer excellent cost-effectiveness over the long term. While the initial material cost may be higher than alternatives like PVC or raw steel, the reduced weight, low maintenance, and long lifespan of aluminum contribute to overall savings across the product lifecycle.

conclusion
ZGGD Metal is your trusted supplier of high-quality aluminum extrusion profiles, providing a variety of shapes and specifications, including Z-shaped aluminum profiles, U-shaped aluminum profiles, H-shaped aluminum profiles, and customized T-shaped aluminum profile solutions. We provide you with high-quality products, flexible payment methods, and reliable inspection reports. Choose the best aluminum profile manufacturer – ZGGD Metal.







