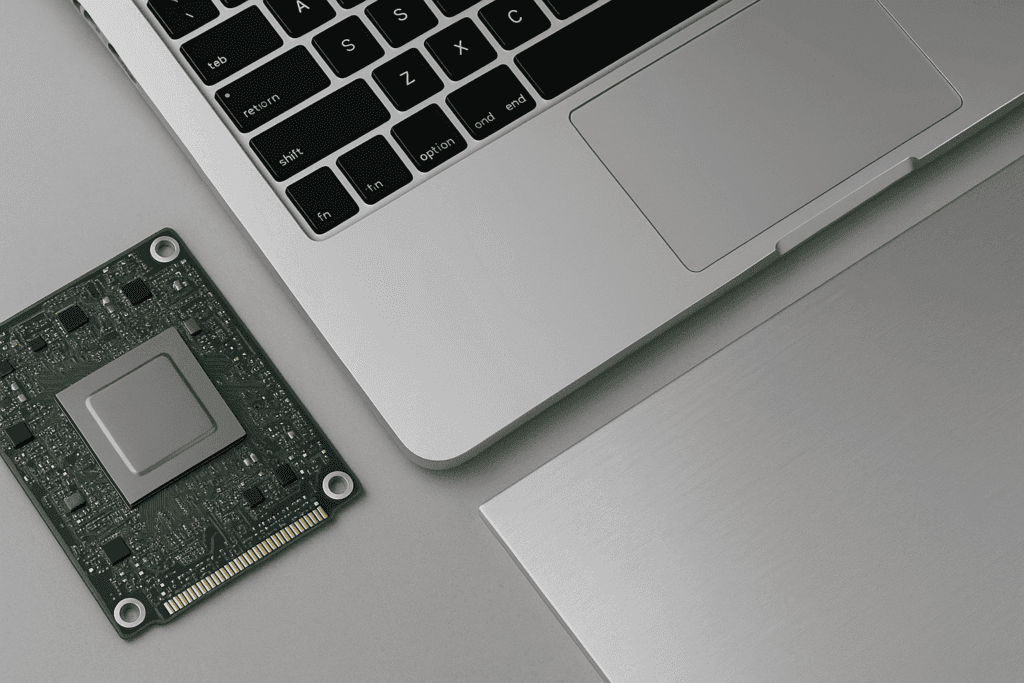
Aluminum is a cornerstone material in the electronics industry, offering an exceptional combination of conductivity, lightweight performance, corrosion resistance, and cost-efficiency. As global demand for compact, high-performance, and energy-efficient devices increases, aluminum’s role in modern electronics becomes even more critical.
This article explores the applications of aluminum in electronics, key advantages, and why manufacturers around the world rely on aluminum tubes, rods, plates, and coils for innovative product development.
Why Aluminum? Key Properties That Drive Electronic Applications
Aluminum’s physical and chemical characteristics make it a preferred choice for electronic components:
- Excellent thermal conductivity (up to 235 W/m·K)
- Good electrical conductivity
- Lightweight (about 2.7g/cm³, one-third the weight of copper)
- Corrosion resistance due to natural oxide layer
- Non-magnetic and non-sparking
- Fully recyclable
These properties ensure aluminum performs well in both consumer electronics and industrial-level devices.
Major Applications of Aluminum in Electronics
1. Aluminum Heat Sinks and Thermal Management Systems
Heat dissipation is critical in electronics. Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity makes it the ideal material for heat sinks, cooling plates, and thermal spreaders used in:
- CPUs and GPUs
- Power modules
- LED lighting systems
- Automotive electronics
Aluminum plates and aluminum extrusions are widely used to produce custom heat sinks in mass volumes.
2. Aluminum Housings and Casings
Consumer electronics—from smartphones to laptops—use aluminum enclosures for:
- Heat dissipation
- Structural integrity
- Aesthetic appeal (sleek, metallic finish)
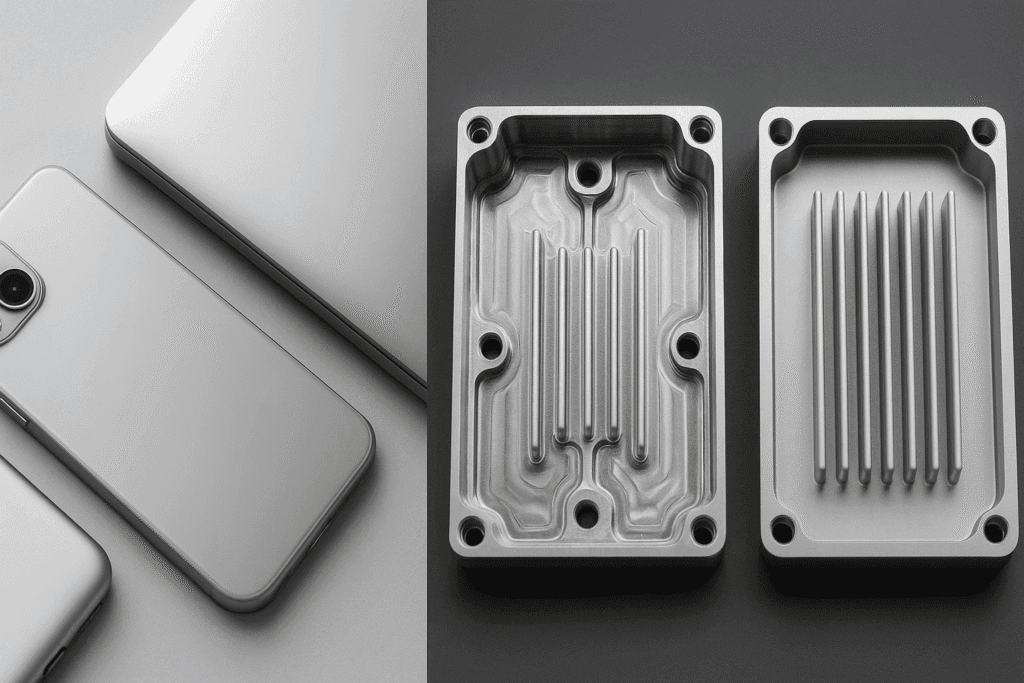
Aluminum sheets and coils are pressed or CNC machined into custom casings, especially in high-end devices like MacBooks, tablets, and audio equipment.
3. Conductive Paths and Busbars
Although copper is traditionally used for high-conductivity applications, aluminum busbars and rods are gaining popularity for power distribution in:
- Data centers
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Battery packs
Aluminum provides a cost-effective, lightweight alternative without compromising conductivity for many medium-voltage applications.
4. Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
Aluminum is used extensively in electrolytic capacitors, a fundamental component in virtually all electronic circuits. Rolled aluminum foils serve as electrodes due to their ability to form a thin, stable, and insulating oxide layer.
5. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
In high-power applications such as LED drivers or power electronics, aluminum-backed PCBs are used to ensure effective heat dissipation. The structure typically involves:
- A thin dielectric layer
- An aluminum base plate
- A copper circuit layer on top
This hybrid construction allows electronics to run cooler and more reliably.
Advantages of Using Aluminum in Electronics Manufacturing
| Advantage | Benefit |
| Weight Reduction | Essential for mobile and wearable devices |
| Thermal Performance | Extends component lifespan |
| Formability | Easy to machine, extrude, and cast |
| Cost-effective | Lower price point compared to copper |
| Environmental | Recyclable and sustainable |
Industries Benefiting from Aluminum-Based Electronics
- Consumer electronics (phones, laptops, tablets)
- Telecommunications (servers, base stations)
- Automotive and EVs (battery enclosures, power modules)
- Renewable energy (inverters, power optimizers)
- Industrial automation (motor drivers, PLCs)
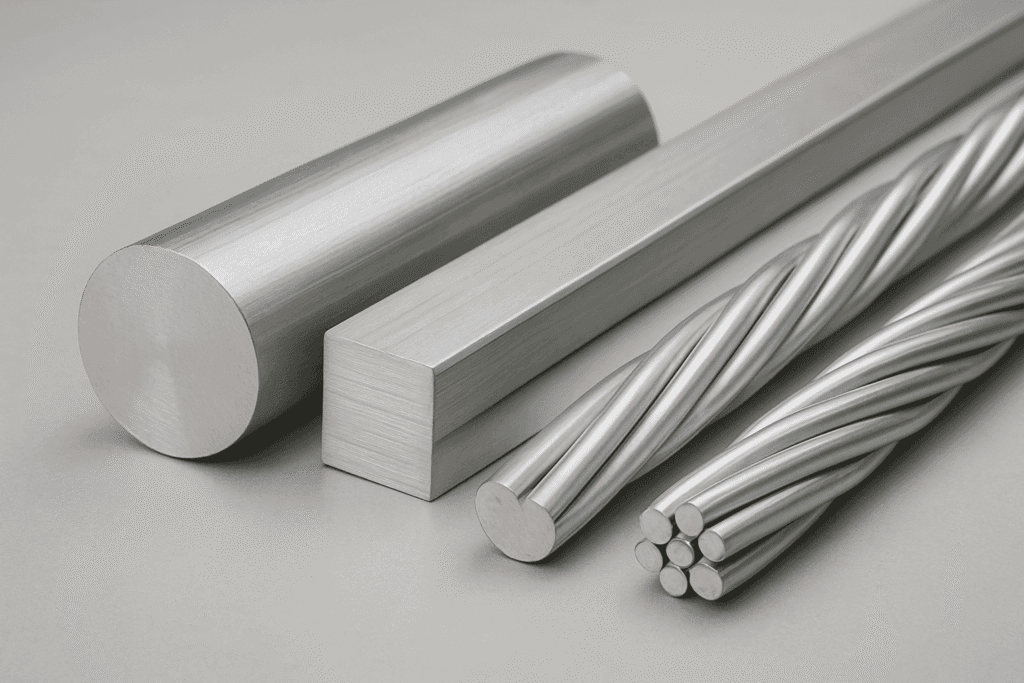
Sourcing Aluminum for Electronics: What to Look For?
When sourcing aluminum materials for electronics, consider the following:
- Alloy type: Common choices include 1050, 1060, 6061, 3003, and 5052 based on conductivity, strength, and corrosion resistance.
- Form: Tubes, rods, plates, coils, foils—each suited for different components.
- Surface treatment: Anodizing, coating, or polishing may be required.
- Tolerances and customization: Precision machining and tight specs ensure fit in electronic assemblies.
Looking for a reliable aluminum supplier? Contact us today to learn about our custom aluminum tubes, rods, sheets, and coils designed for electronics manufacturers.
Conclusion
As electronic devices become more compact and thermally demanding, aluminum continues to play a critical role across thermal, structural, and conductive functions. From heat sinks to enclosures, busbars to PCBs, its applications are as diverse as the industries it supports.
Investing in high-quality aluminum materials ensures long-term performance, cost savings, and sustainability. Whether you’re designing the next generation of consumer devices or scaling up EV production, aluminum is an essential element of your material strategy.






